
笔者在apache-issue提出了该问题,目前解决方案正在讨论中 https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/LOG4J2-2490
前言
日志应该是一个应用的基础组件, 其中老牌的log4j应该是我们用的最多的, 后来互联网发展,大家都朝着高并发的方向发力,发现log4j性能不行,因为竞争锁导致阻塞,性能跟不上. 后来其创始人另立门户logback后, log4j的新主子Apache进行了大的升级改造,就是如今的log4j2, 其异步日志的性能也是一骑绝尘, 然而其使用过程中依然有很多坑,稍不留意就会搞个人仰马翻. 下面先列举一些别人踩过的log4j的坑:
问题描述
初级表现
一个APP推送服务,在一次发布之后, 当遇到批量推送任务时, 线程池打满, 队列打满, 任务堆积. (注: 由于该次发布的改动点很普通, 没有先怀疑该点.)
相关环境
- spring-boot: 1.5.3
- log4j: 2.7
- jdk1.8
发布改动点
- 新增了一个功能 (和本次内容无关)
- 在一个类上加了
@RefreshScope 注解
处理流程
- 原以为是第三方接口耗时增加导致的, 监控显示耗时确实挺高,但是通过ping,curl,网络监控等手段发现并不是接口问题
- 阅读代码发现那个监控项不仅包含了调用第三方接口的耗时,还有其它操作, 遂认为该监控不可信,再次验证不是第三方接口,也不是网络的问题
- 发现统计日志中的两个时间点差异比较大,竟然有三秒. 关键是这两个时间点之间只是抛了个异常,然后打了个日志
- 在代码中发现log4j2配置用的是同步Logger,异步AsyncAppender,怀疑是高并发时同步日志产生的阻塞, 将日志改为配合disrupter的AsyncLogger,结果没有什么用
- 进行Thread Dump发现很多线程BLOCKED,调用栈显示确实是与log4j有关, 并且明显指向和异常栈打印有关
- 由于应用中有很多警告, 并且这些日志都把异常栈打印出来了. 于是将日志中不必要的异常栈都停止打印, 之后问题解决
问题分析
疑问点
- 日志为什么没有走异步打印?
- 为什么打印异常栈会阻塞? 阻塞在什么地方?
- 为什么会引起阻塞,和发布的改动点有哪些联系?
线程栈分析
以下日志为改为异步日志(AsyncLogger)之后的阻塞线程栈,可以发现日志并没有用到disruptor这个无锁库,而是转为了同步Logger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
"fastExecutor-670" #2178 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x00007f2d483cd800 nid=0x6026 waiting for monitor entry [0x00007f2c158c3000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:404)
- waiting to lock <0x0000000088104b60> (a java.lang.Object)
at org.springframework.boot.loader.LaunchedURLClassLoader.loadClass(LaunchedURLClassLoader.java:94)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:357)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.loadClass(ThrowableProxy.java:539)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.toExtendedStackTrace(ThrowableProxy.java:660)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.<init>(ThrowableProxy.java:137)
at org.springframework.boot.loader.LaunchedURLClassLoader.loadClass(LaunchedURLClassLoader.java:94)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:357)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.loadClass(ThrowableProxy.java:539)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.toExtendedStackTrace(ThrowableProxy.java:660)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.<init>(ThrowableProxy.java:137)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.<init>(ThrowableProxy.java:121)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.Log4jLogEvent.getThrownProxy(Log4jLogEvent.java:555)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.pattern.ExtendedThrowablePatternConverter.format(ExtendedThrowablePatternConverter.java:61)
... 精简部分日志 ...
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.LoggerConfig.callAppenders(LoggerConfig.java:447)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.async.AsyncLoggerConfig.callAppendersInCurrentThread(AsyncLoggerConfig.java:105)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.async.EventRoute$2.logMessage(EventRoute.java:65)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.async.AsyncLoggerConfig.callAppenders(AsyncLoggerConfig.java:95)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.LoggerConfig.processLogEvent(LoggerConfig.java:432)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.LoggerConfig.log(LoggerConfig.java:416)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.LoggerConfig.log(LoggerConfig.java:402)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.config.AwaitCompletionReliabilityStrategy.log(AwaitCompletionReliabilityStrategy.java:63)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.Logger.logMessage(Logger.java:146)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger.logMessageSafely(AbstractLogger.java:2091)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger.logMessage(AbstractLogger.java:1988)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger.logIfEnabled(AbstractLogger.java:1960)
at org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLogger.warn(Log4jLogger.java:259)
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.traffic.FastCommander.lambda$runnersEnter$0(FastCommander.java:175)
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.traffic.FastCommander$$Lambda$111/638548222.run(Unknown Source)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1142)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:617)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
|
以下为应用异常栈内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
com.dianwoda.delibird.common.domain.DeliException:
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.manager.PushManager.send(PushManager.java:104) ~[classes!/:?]
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor119.invoke(Unknown Source) ~[?:?]
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ~[?:1.8.0_77]
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) ~[?:1.8.0_77]
at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(ReflectionUtils.java:216) ~[spring-core-4.3.15.RELEASE.jar!/:4.3.15.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cloud.context.scope.GenericScope$LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean.invoke(GenericScope.java:472) ~[spring-cloud-context-1.3.3.RELEASE.jar!/:1.3.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:179) ~[spring-aop-4.3.15.RELEASE.jar!/:4.3.15.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.intercept(CglibAopProxy.java:673) ~[spring-aop-4.3.15.RELEASE.jar!/:4.3.15.RELEASE]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.manager.PushManager$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$74851038.send(<generated>) ~[classes!/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.provider.DeliPushProviderImpl.lambda$send$0(DeliPushProviderImpl.java:84) ~[classes!/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.tool.DeliRunnable.run(DeliRunnable.java:26) ~[delibird-common-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar!/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.traffic.FastCommander.lambda$runnersEnter$0(FastCommander.java:173) ~[delibird-common-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar!/:?]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1142) [?:1.8.0_77]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:617) [?:1.8.0_77]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745) [?:1.8.0_77]
|
疑问点一
日志为什么没有走异步打印?
Log4j2中默认会优先尝试将LogEvent放入RingBuffer中,如果放不进去(原因大概是队列已满),则会通过AsyncQueueFullPolicy(可自定义)来决策下一步行为(EventRoute:丢弃 - discard,同步 - synchronous,等待入队 - enqueue),在log4j-2.7中默认是同步写日志(2.9中默认是等待入队Enqueue的方式),因此,当日志量突增时,异步日志变同步日志!
疑问点二
为什么打印异常栈会阻塞? 阻塞在什么地方?
根据线程栈, 问题主要是因为org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.toExtendedStackTrace这个方法. 其中ThrowableProxy这个类是因为LogEvent可能会被跨网络传输,而LogEvent中的异常栈可能不会被另一端识别,因此需要对异常栈进行重新封装,会取出栈中异常的jar包及版本等信息。该类的注释如下:
包装一个Throwable并添加每个堆栈跟踪元素的包信息。
用于在不同ClassLoader或JVM中表示Throwable的一个代理,当应用反序列化一个ThrowableProxy, Throwable也许没有被设置,但是Throwable信息被保存在该代理的其它字段,像 message和stack trace
另外该方法是为了"解析此堆栈跟踪中与父元素不同的所有堆栈条目", 简单的讲,就是把异常堆栈与当前的线程栈作对比,把异常堆栈中不一样的类信息解析出来,包括类名,行号,包名,包版本等信息,这时候就需要根据异常栈中的类名获取Class对象,便需要类加载. 根据线程栈来分析下类加载的过程, 可以看到阻塞的地方是在等待一个锁, 正是因为锁等待导致打印日志的操作耗时3s.
以下为阻塞线程的线程栈:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:404)
- waiting to lock <0x0000000088104b60> (a java.lang.Object)
at org.springframework.boot.loader.LaunchedURLClassLoader.loadClass(LaunchedURLClassLoader.java:94)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:357)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.loadClass(ThrowableProxy.java:539)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.toExtendedStackTrace(ThrowableProxy.java:660)
|
以下为类加载获取锁的代码片段: code-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
// java.lang.ClassLoader#loadClass(java.lang.String, boolean)
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) { // 源码行号:404
//(1. 注: 先从jvm检查下类加载过没有,已加载就直接返回该对象,防止类重复加载)
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
// 2. 如果该类加载器有父对象,先用父加载器加载,这就是双亲委派机制
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
// 3. 如果父加载器加载不到,就用引导加载器加载
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// 4. 如果前面双亲都没有加载到, 采用当前自定义的findClass加载
c = findClass(name); // 源码行号:424
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
|
可以看到类加载的时候会先用检查下是否已经加载过,加载过就直接返回jvm中的类对象. 如果是走的是获取加载过的类,应该是非常快的,因为仅仅是一个内存操作,获取的锁会被马上释放, 在几千QPS的情况下根本不可能发生阻塞3s这样的事情, 那么此时的类到底有没有被加载过呢?
可以看下获取到该锁 0x0000000088104b60 的线程栈:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
"fastExecutor-671" #1739 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x00007f2d00015000 nid=0x5e64 runnable [0x00007f2c237f9000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at sun.misc.URLClassPath$Loader.getResource(URLClassPath.java:702)
at sun.misc.URLClassPath.getResource(URLClassPath.java:212)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:365)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:362)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:361)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:424)
- locked <0x0000000088104b60> (a java.lang.Object)
at org.springframework.boot.loader.LaunchedURLClassLoader.loadClass(LaunchedURLClassLoader.java:94)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:357)
at org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy.loadClass(ThrowableProxy.java:539)
... 精简部分内容 ...
|
根据上面的线程栈, 获取锁之后走到源码的424行, 就表示类没有在jvm中加载过,并且双亲加载器也加载不到,调用了findClass去加载. 这里就非常奇怪了, jvm如果加载过一次,下次一定会从jvm中直接拿到, 结合前面说的锁会马上释放, 根本不会阻塞. 也就是说实际每次要重新加载. 为了找到具体是哪个类每次都需要加载一次,需要来debug确定.
下面是log4j2中 ThrowableProxy 类加载流程的代码: code-2 ,是调用类加载的地方.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
// org.apache.logging.log4j.core.impl.ThrowableProxy#loadClass(java.lang.String)
/**
* Loads classes not located via Reflection.getCallerClass.
*
* @param lastLoader The ClassLoader that loaded the Class that called this Class.
* @param className The name of the Class.
* @return The Class object for the Class or null if it could not be located.
*/
private Class<?> loadClass(final ClassLoader lastLoader, final String className) {
// XXX: this is overly complicated (注:确实过于复杂,哈哈哈)
Class<?> clazz;
if (lastLoader != null) {
try {
// 1. 先用ClassLoader加载一下, 加载上就返回
clazz = lastLoader.loadClass(className); // 源码行号: 539
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
} catch (final Throwable ignore) {
// Ignore exception.
}
}
try {
// 2. 上一步没加载上,或者出现异常,用LoaderUtil再次加载(使用Class.forName以及当前线程的ClassLoader)
clazz = LoaderUtil.loadClass(className);
} catch (final ClassNotFoundException | NoClassDefFoundError e) {
// 3. 加载出现异常,再次尝试一种加载方式
return loadClass(className);
} catch (final SecurityException e) {
return null;
}
return clazz;
}
// 4. 接上面的3, 再次用当前对象类的加载器加载,出现异常返回空
private Class<?> loadClass(final String className) {
try {
return this.getClass().getClassLoader().loadClass(className);
} catch (final ClassNotFoundException | NoClassDefFoundError | SecurityException e) {
return null;
}
}
|
调试过程
先让代码跑起来,并走几次出问题的流程,确保该加载的类已经加载过了, 然后在 code-1 中 findLoadedClass 方法处打断点并查看返回值是否为空. code-2 中lastLoader的类型是LaunchedURLClassLoader 继承关系如下图
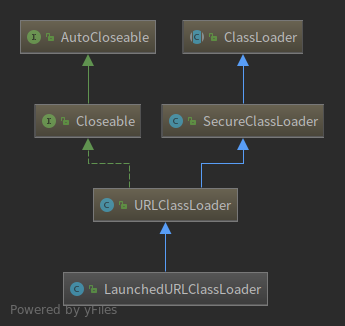
loadClass 方法如: code-3 : org.springframework.boot.loader.LaunchedURLClassLoader#loadClass
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
@Override
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
Handler.setUseFastConnectionExceptions(true);
try {
try {
definePackageIfNecessary(name);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
// Tolerate race condition due to being parallel capable
if (getPackage(name) == null) {
// This should never happen as the IllegalArgumentException indicates
// that the package has already been defined and, therefore,
// getPackage(name) should not return null.
throw new AssertionError("Package " + name + " has already been "
+ "defined but it could not be found");
}
}
return super.loadClass(name, resolve);
}
finally {
Handler.setUseFastConnectionExceptions(false);
}
}
|
执行 lastLoader.loadClass(className) 跳到 code-1 , 整个加载流程遵循双亲委派机制, 如下图
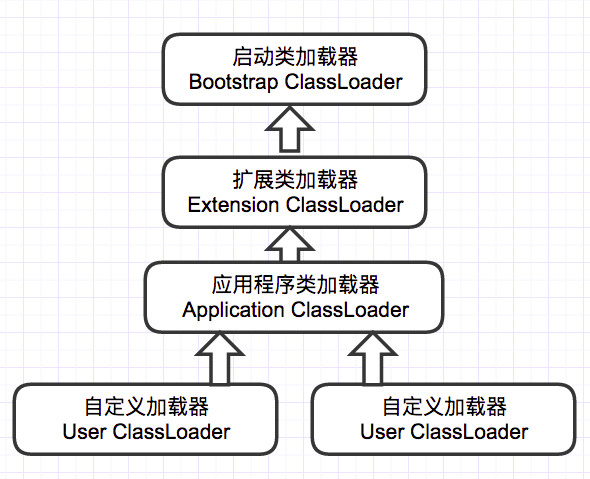
LaunchedURLClassLoader是一个自定义类加载器, 直接调用父类 ClassLoader#loadClass 即 code-1 中所示, 分别用“应用类加载器”、“扩展类加载器”、“引导类加载器”加载,最终发现了当出现类名 sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor204 时经过 parent loaders、bootstrap loader、URLClassLoader#findClass都加载不到,最后抛出ClassNotFoundException被 code-2 步骤1处捕获并忽略,接着执行步骤2继续尝试加载,随后抛出异常,捕获后在步骤3处再次尝试加载,再次异常返回空。
如异常日志at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor119.invoke(Unknown Source) ~[?:?], 由于加载不到该类,源码信息、包信息都是没有的。
插曲: 调试过程中重启了一次应用,发现再也走不到之前的调试逻辑了,好像所有的事情都正常了,没有加载不上的类了,顿时一脸懵逼。然后误打误撞,用一个批量调用的脚本吭哧吭哧一顿调用,然后问题又重现了
在准备看看sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor204这个类为什么加载不上时,发现根本没有这个类,一看类名就怀疑是反射生成的类。加上之前的插曲,另外还有别人的提醒,以及google,发现根本原因竟是jvm对反射的优化策略。
jvm对反射的优化
jvm对待反射有两种方式:
- 使用native方法进行反射操作,这种方式每次执行的速度差不多
- 生成bytecode进行反射操作,即生成类
sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor<N>,它是一个被反射调用方法的包装类,代理不同的方法,类后缀序号会递增。这种方式第一次调用速度较慢,较之第一种会慢3-4倍,但是多次调用后速度会提升20倍
在ReflectionFactory里有一种机制,就是当一个方法被反射调用的次数超过一定的阀值时(inflationThreshold),会使用第二种方式来提升速度。这个阀值的默认值是15.该阈值可以通过jvm参数-Dsun.reflect.inflationThreshold进行配置。
那么为什么log4j2不能加载到生成类sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor<N>呢?
要回答这个问题就要了解jvm反射实现的第二种方式,jvm会通过方法sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory#newMethodAccessor构建MethodAccessor,代理通过该对象的invoke方法调用真正的方法。下图为MethodAccessor接口的相关实现类
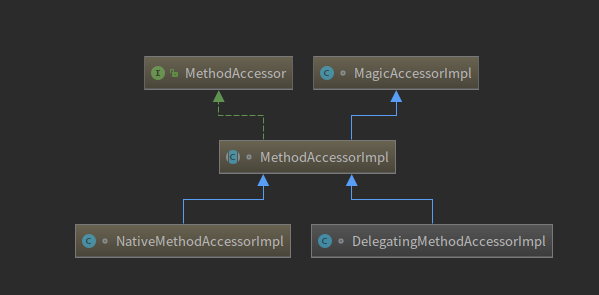
ReflectionFactory#newMethodAccessor代码如下: code-4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public MethodAccessor newMethodAccessor(Method method) {
checkInitted();
// noInflation(不膨胀),直接使用字节码增强方式
if (noInflation && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
} else {
// 否则使用Inflation膨胀模式, 先创建NativeMethodAccessorImpl,随后将该实现作为DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl的一个delegate,实际上还是委派给NativeMethodAccessorImpl
NativeMethodAccessorImpl acc =
new NativeMethodAccessorImpl(method);
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl res =
new DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(acc);
acc.setParent(res);
return res;
}
}
|
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl#invoke代码如下: code-5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
// We can't inflate methods belonging to vm-anonymous classes because
// that kind of class can't be referred to by name, hence can't be
// found from the generated bytecode.(我们不能膨胀属于vm-anonymous的类,因为这种类不能通过名字引用,因此不能从生成的字节码中被发现)
//
// 这里可以看到,如果调用次数大于inflationThreshold就会膨胀,使用字节码增强的方式
if (++numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold()
&& !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
MethodAccessorImpl acc = (MethodAccessorImpl)
new MethodAccessorGenerator().
generateMethod(method.getDeclaringClass(),
method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getExceptionTypes(),
method.getModifiers());
parent.setDelegate(acc);
}
// 没有超过膨胀阈值,就使用JNI方法
return invoke0(method, obj, args);
}
|
继续查看代码,可以看到sun.reflect.MethodAccessorGenerator#generate的实现是调用asm字节码增强工具来生成类,此过程较长,不在此列出。在该方法的最后,我们发现有这样一个操作sun.reflect.ClassDefiner#defineClass,查看其源码
defineClass代码如下: code-6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
/** <P> We define generated code into a new class loader which
delegates to the defining loader of the target class. It is
necessary for the VM to be able to resolve references to the
target class from the generated bytecodes, which could not occur
if the generated code was loaded into the bootstrap class
loader. </P>
<P> There are two primary reasons for creating a new loader
instead of defining these bytecodes directly into the defining
loader of the target class: first, it avoids any possible
security risk of having these bytecodes in the same loader.
Second, it allows the generated bytecodes to be unloaded earlier
than would otherwise be possible, decreasing run-time
footprint. </P>
*/
static Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] bytes, int off, int len,
final ClassLoader parentClassLoader)
{
// 创建一个DelegatingClassLoader用来加载生成的类
ClassLoader newLoader = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<ClassLoader>() {
public ClassLoader run() {
return new DelegatingClassLoader(parentClassLoader);
}
});
return unsafe.defineClass(name, bytes, off, len, newLoader, null);
}
|
通过上面代码及注释,发现生成的类是绑定在DelegatingClassLoader这个加载器上的,也就是说只有通过该加载器才能load生成的类,然而在log4j的ThrowableProxy#loadClass方法并没有尝试该类加载器,所以加载不到也是很正常的了。
疑问点三
为什么会引起阻塞,和发布的改动点有哪些联系?
分析至此,引起阻塞的原因就清楚了,是因为jvm对待反射的优化,使得动态生成的类始终不能通过classLoader加载,于是每次解析异常栈都会进行类加载,并且由于双亲委派和ThrowableProxy#loadClass的多次异常处理,导致锁占有的时间很长,最终导致阻塞。
关于发布改动点,就是加上了@RefreshScope注解,通过对比加了和没加的异常栈日志,也发现了差别。
没有加@RefreshScope注解的异常栈:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
com.dianwoda.delibird.common.domain.DeliException:
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.manager.PushManager.send(PushManager.java:104) ~[classes/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.provider.DeliPushProviderImpl.lambda$send$0(DeliPushProviderImpl.java:84) ~[classes/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.tool.DeliRunnable.run(DeliRunnable.java:26) ~[classes/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.traffic.FastCommander.lambda$runnersEnter$0(FastCommander.java:174) ~[classes/:?]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149) [?:1.8.0_161]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624) [?:1.8.0_161]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) [?:1.8.0_161]
|
加了@RefreshScope注解的异常栈:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
com.dianwoda.delibird.common.domain.DeliException:
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.manager.PushManager.send(PushManager.java:104) ~[classes/:?]
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor204.invoke(Unknown Source) ~[?:?]
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ~[?:1.8.0_161]
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) ~[?:1.8.0_161]
at org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(ReflectionUtils.java:216) ~[spring-core-4.3.15.RELEASE.jar:4.3.15.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.cloud.context.scope.GenericScope$LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean.invoke(GenericScope.java:472) ~[spring-cloud-context-1.3.3.RELEASE.jar:1.3.3.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:179) ~[spring-aop-4.3.15.RELEASE.jar:4.3.15.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.intercept(CglibAopProxy.java:673) ~[spring-aop-4.3.15.RELEASE.jar:4.3.15.RELEASE]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.manager.PushManager$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$14df0707.send(<generated>) ~[classes/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.push.provider.DeliPushProviderImpl.lambda$send$0(DeliPushProviderImpl.java:84) ~[classes/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.tool.DeliRunnable.run(DeliRunnable.java:26) ~[classes/:?]
at com.dianwoda.delibird.common.traffic.FastCommander.lambda$runnersEnter$0(FastCommander.java:174) ~[classes/:?]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149) [?:1.8.0_161]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624) [?:1.8.0_161]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) [?:1.8.0_161]
|
@RefreshScope的原理
该注解是spring-cloud中用来在配置更新后刷新bean,其原理如下:
- @RefreshScope 内嵌入了@Scope注解, 用于Spring Scope机制,即是把bean分成不同类型,控制Bean如何通过BeanFactory返回。
- 通过
RefreshScope的父类方法GenericScope#postProcessBeanFactory把自己注册到beanFactory中,而实现了Scope接口的GenericScope#get的方法,会在get时放入StandardScopeCache缓存中, 其实声明了RefreshScope的bean都是懒加载,在初次使用时才进行创建并缓存。
- 当调用
RefreshScope#refresh方法时,先从缓存中删除先前的Bean,然后再执行GenericScope.BeanLifecycleWrapper#destroy方法彻底结束上一个Bean生命周期,然后再发布一个RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent事件。
- 当一个Bean的method被调用的时候,由于这个bean是被代理的,会触发
org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept方法,方法中会调用org.springframework.aop.target.SimpleBeanTargetSource#getTarget重新生成一个bean 放入 StandardScopeCache中,从而实现了bean更新
从上面的原理看出经过@RefreshScope注解过的bean就是一个代理,这也不难理解为什么会用到反射,然后由于jvm对反射的优化而产生该问题
总结
该问题的原因,其实有很多方面:
- 从表面看来是加了个
@RefreshScope注解导致的
- 从自身看来是打了太多异常栈
- 从log4j来看是
log4j 2.7的队列满了之后的默认处理策略问题
- 另外对于log4j看来其实是一个需要优化的地方,对于动态生成的类就应该特殊处理,选择正确的类加载器,或者不进行类加载
参考



