前面讲了空间搜索的两个常用原理,应该还算是比较容易理解的,毕竟只是算法,并不需要我们来实现,我们通过简单地配置就可以用上Solr的空间搜索的功能。下面就来讲讲如何配置空间搜索。
前面说的GeoHash和Cartesian Tiers原理,在Solr中对应的是实现分别是GeohashPrefixTree类和QuadPrefixTree类,通过这两个类在数据索引阶段按照两个不同的原理进行索引的建立。Solr中默认是使用GeohashPrefixTree的方式。
索引的构建
通过前面的Solr5配置文件参数解析一文,我们应该了解到建立索引,首先我们以该先配置field,这里也一样,要想对空间信息(即坐标)进行索引,首先我们应该先配置坐标的field。
配置项和参数说明
需要配置fieldType和field两项。
1
2
3
|
<fieldType name="location_rpt" class="solr.SpatialRecursivePrefixTreeFieldType" spatialContextFactory="com.spatial4j.core.context.jts.JtsSpatialContextFactory" distErrPct="0.025" maxDistErr="0.000009" units="degrees"/>
<field name="sight_coordinate" type="location_rpt" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="false" />
|
这些配置项的一些属性,下面做一些说明:
SpatialRecursivePrefixTreeFieldType
用于深度遍历前缀树的FieldType,主要用于获得基于Lucene中的RecursivePrefixTreeStrategy。
JtsSpatialContextFactory
当有Polygon多边形或者linestrings线段时,会使用jts(需要把jts.jar放到solr服务的lib下),而基本形状使用SpatialContext (spatial4j的类)。
distErrPct
定义非Point图形的精度,范围在0-0.5之间。该值决定了非Point的图形索引或查询时的level(如geohash模式时就是geohash编码的长度)。当为0时取maxLevels,即精度最大,精度越大将花费更多的空间和时间去建索引。
geo
默认为true,值为true的情况下坐标基于球面坐标系,采用Geohash的方式;值为false的情况下坐标基于2D平面的坐标系,采用Euclidean/Cartesian的方式。
worldBounds
世界坐标值:”minX minY maxX maxY”。 geo=true即geohash模式时,该值默认为”-180 -90 180 90”。geo=false即quad时,该值为Java double类型的正负边界,此时需要指定该值,设置成”-180 -90 180 90”。
distCalculator
设置距离计算算法,geo=true默认是haversine,geo=false默认是cartesian(笛卡尔计算方式),值可以为"lawOfCosines"(余弦定理), “vincentySphere”(文森特球面公式) 或 “cartesian^2”。
prefixTree
Solr将地球映射为网格,prefixTree定义了网格的实现方式,每个网格在下一层中可以分解成多个子网格,geo=true prefixTree只能取GeoHash,geo=false prefixTree可取quad(quadTree一种四分树地理位置索引,对应笛卡尔分层策略)
maxDistErr/maxLevels
maxDistErr定义了索引数据的最高层maxLevels,上述定义为0.000009,根据GeohashUtils.lookupHashLenForWidthHeight(0.000009, 0.000009)算出编码长度为11位,精度在1米左右,直接决定了Point索引的term数。
maxLevels优先级高于maxDistErr,即有maxLevels的话maxDistErr失效。详见SpatialPrefixTreeFactory.init()方法。不过一般使用maxDistErr。
units
单位是degrees,不适用于geofilt, bbox, or geodist(单位为km)
用代码构建索引
1
2
3
4
5
|
doc.setField("poi_location_p", "32.52162,120.31778") //point类型
//或者
doc.setField("poi_location_p", "POLYGON((120.35330414772034
31.58268495951037,120.35190939903259 31.57923921490961,120.35330414772034
31.58268495951037))") //多边形类型
|
构建流程:
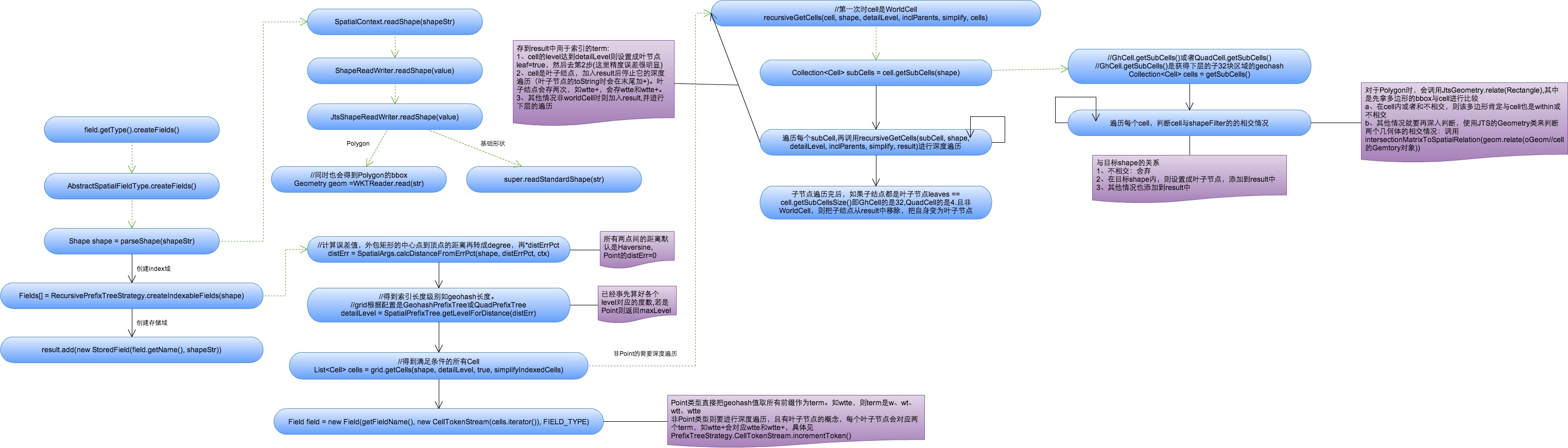
下面主要说明Point类型的term创建过程。
1、将空间索引域的shapeStr解析成相应的Shape(这里指Point,复杂Shape如Polygon要使用JTS中的WTKReader来解析)。
2、创建索引域,具体过程参考org.apache.lucene.spatial.prefix.RecursivePrefixTreeStrategy中的createIndexableFields方法。
a、根据distErrPct字段,计算距离的误差值,对于Point来说默认为0(而对于非Point类型来说,是通过外包矩形中心点到矩形顶点的距离再乘以distErrPct来计算误差值的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
double distErr = SpatialArgs.calcDistanceFromErrPct(shape, distErrPct, ctx);
public static double calcDistanceFromErrPct(Shape shape, double distErrPct, SpatialContext ctx) {
if (distErrPct < 0 || distErrPct > 0.5) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("distErrPct " + distErrPct + " must be between [0 to 0.5]");
}
if (distErrPct == 0 || shape instanceof Point) {
return 0;
}
Rectangle bbox = shape.getBoundingBox();
//Compute the distance from the center to a corner. Because the distance
// to a bottom corner vs a top corner can vary in a geospatial scenario,
// take the closest one (greater precision).
Point ctr = bbox.getCenter();
double y = (ctr.getY() >= 0 ? bbox.getMaxY() : bbox.getMinY());
double diagonalDist = ctx.getDistCalc().distance(ctr, bbox.getMaxX(), y);
return diagonalDist * distErrPct;
}
|
b、根据上述计算出的误差值,得到索引的geohash编码长度,对于Point类型来说值为maxLevels。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public int getLevelForDistance(double dist) {
if (dist == 0)
return maxLevels;//short circuit
final int level = GeohashUtils.lookupHashLenForWidthHeight(dist, dist);
return Math.max(Math.min(level, maxLevels), 1);
}
|
c、根据编码长度得到满足所有条件的cells(每个cell表示一个前缀值),并将Cells都放在CellTokenStream中,同时构建索引域。Point类型每个Cell表示geohash的一个前缀值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public List<Cell> getCells(Point p, int detailLevel, boolean inclParents){
Cell cell = getCell(p, detailLevel);
if (!inclParents) {
return Collections.singletonList(cell);
}
String endToken = cell.getTokenString();
assert endToken.length() == detailLevel;
List<Cell> cells = new ArrayList<Cell>(detailLevel);
for (int i = 1; i < detailLevel; i++) {
cells.add(getCell(endToken.substring(0, i)));
}
cells.add(cell);
return cells;
}
Field field = new Field(getFieldName(),
new CellTokenStream(cells.iterator()), FIELD_TYPE);
|
3、构建存取域存储索引
1
2
3
4
5
|
if (field.stored()) {
if (shapeStr == null)
shapeStr = shapeToString(shape);
result.add(new StoredField(field.getName(), shapeStr));
}
|
4、结果
如经纬度41.79452,123.41555,对应的geohash为wxrvb2kqexu(maxLevels=11), 则其对应的term有11个(如w、wx、wxr、wxrv…)。
查询
这这里之前,请确保已经已经看过查询方法及参数说明//TODO这篇文章,对查询常用到的参数比较熟悉。
查询语法实例:
1
2
3
4
|
q={!geofilt pt=45.15,-93.85 sfield=poi_location_p d=5 score=distance}
q={!bbox pt=45.15,-93.85 sfield=poi_location_p d=5 score=distance}
q=poi_location_p:"Intersects(-74.093 41.042 -69.347 44.558)" //a bounding box (not in WKT)
q=poi_location_p:"Intersects(POLYGON((-10 30, -40 40, -10 -20, 40 20, 0 0, -10 30)))" //a WKT example
|
空间搜索涉及到的特有的查询参数有:
sfield:指定坐标索引字段,如sfield=geo
pt:坐标点,如pt=54.729696,-98.525391
其中有几种常见的Solr支持的几何操作:
WITHIN:在内部
CONTAINS:包含关系
DISJOINT:不相交
Intersects:相交(存在交集)
我的这个项目实现了范围搜索和图形搜索,其中范围搜索用的是圆形范围,图形搜索用的是矩形边界搜索。更加详细的内容请看美团的文章。
参考资料
- Solr空间搜索原理分析与实践 - 美团

